this post was submitted on 25 Aug 2024
571 points (98.6% liked)
Map Enthusiasts
3463 readers
95 users here now
For the map enthused!
Rules:
-
post relevant content: interesting, informative, and/or pretty maps
-
be nice
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
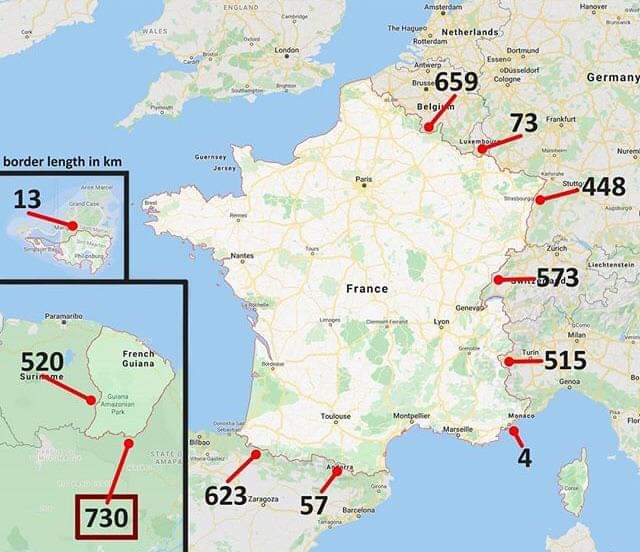
Arnt most borders fractals so can any border be the largest?
considers
Well, they aren't fractal, that's for sure.
It is true that we could make borders more-closely-map to physical features, and that would increase the length somewhat.
And we can define borders however we want, so that's up to us.
But ultimately, matter is quantum, not continuous, so if we're going to link the definition of a border to some function of physical reality, I don't think that we can make a border arbitrarily long.
Well, quantum mechanics is continuous, just in a way that often maps to discrete things when measured. I'm sure someone has written a research paper on quantum law, but I wonder if anyone who actually knows quantum mechanics has.
It is only continuous because it is random, so prior to making a measurement, you describe it in terms of a probability distribution called the state vector. The bits 0 and 1 are discrete, but if I said it was random and asked you to describe it, you would assign it a probability between 0 and 1, and thus it suddenly becomes continuous. (Although, in quantum mechanics, probability amplitudes are complex-valued.) The continuous nature of it is really something epistemic and not ontological. We only observe qubits as either 0 or 1, with discrete values, never anything in between the two.
Sure, but if you measure if a particle is spin up or spin down in a fixed measurement basis, physically rotate the particle, and then measure again the amplitudes change continuously. You could also measure it in another basis, which themselves form a continuous family, and get a similarly logical answer (although not independently of the first one). I don't know much about quantum field theory, but I do know that fields in it are continuous, just like they are in classical theories.
All in all, while quantum logic is part of what makes it continuous, I think I'd still stand by that it is continuous.