Just thought I'd let y'all know, still here, just been browsing for a while, lol
18 naked cowboys practicing social distancing alone in their homes on FaceTime
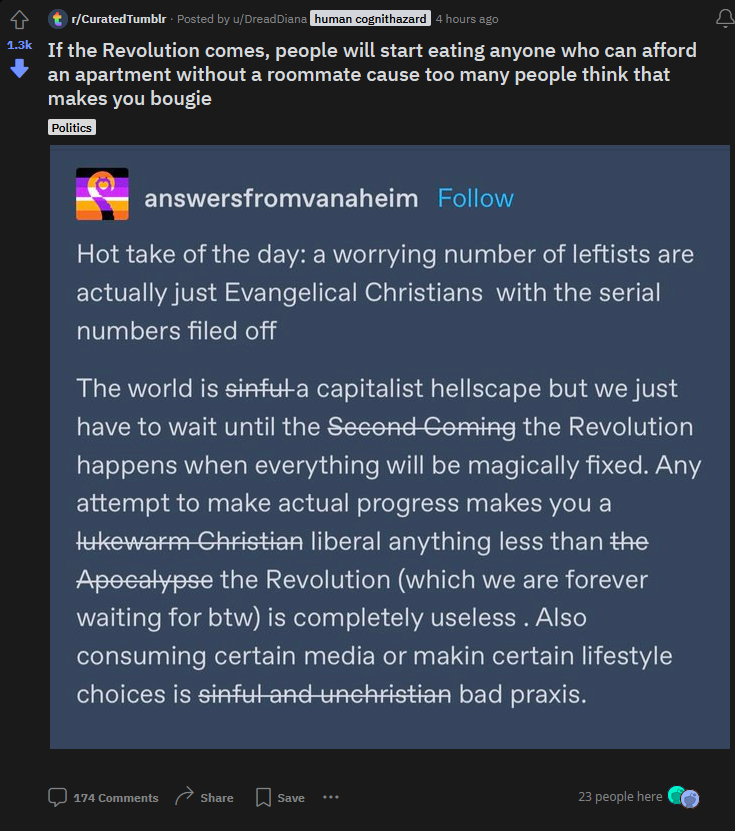
 we're never getting change outside of third worldism bruh
we're never getting change outside of third worldism bruh
source link: https://www.reddit.com/r/CuratedTumblr/comments/1akcbol/if_the_revolution_comes_people_will_start_eating/


The Yakovlev Yak-3 was a single-engine, single-seat World War II Soviet fighter. Robust and easy to maintain, it was much liked by both pilots and ground crew. One of the smallest and lightest combat fighters fielded by any combatant during the war, its high power-to-weight ratio gave it excellent performance and it proved to be a formidable dogfighter.
Lighter and smaller than the Yak-9 but powered by the same engine, the Yak-3 was a forgiving, easy-to-handle aircraft loved by both novice and experienced pilots. It was robust, easy to maintain and a highly successful dog-fighter. It was used mostly as a tactical fighter, flying low over battlefields and engaging in dogfights below 4,000 m (13,000 ft).
The first 197 Yak-3 were lightly armed with a single motornaya pushka-mount 20 mm (0.79 in) ShVAK cannon and one 12.7 mm (0.50 in) UBS synchronized machine gun, with subsequent aircraft receiving a second UBS for a weight of fire of 2.72 kg (6.0 lb) per second using high-explosive ammunition. All armament was installed close to the axis of the aircraft with a cannon mounted in the engine "vee" firing through the propeller boss, synchronised machine guns in the fuselage, helping accuracy and leaving wings unloaded.
Marcel Albert, a World War II French ace who flew the Yak-3 in the USSR with the Normandie-Niémen Group, considered it a superior aircraft to the P-51D Mustang and Supermarine Spitfire. It was also flown by Polish Air Forces (of the Polish People's Army formed in USSR) and the Yugoslav Air Force, after the war.
If you ever want to make your own megathread, you can go here to reserve a spot! :xinternet:
Resources for Organizing your workplace/community :sabo:
Resources for Palestine :palestine-heart:
Buy coffee and learn more about the Zapatistas in Chiapas here :EZLN:
Here are some resources on Prison Abolition :brick-police:
Foundations of Leninism :USSR:
:lenin-shining: :unity: :kropotkin-shining:
Anarchism and Other Essays :ancom:
Remember, sort by new you :LIB:
Follow the Hexbear twitter account :comrade-birdie:
THEORY; it’s good for what ails you (all kinds of tendencies inside!) :RIchard-D-Wolff:
Come listen to music with your fellow Hexbears in Cy.tube :og-hex-bear:
Queer stuff? Come talk in the queer megathread!! :sicko-queer:
Monthly Neurodiverse Megathread and Monthly ND Venting Thread :Care-Comrade:

Phạm Tuân born 14 February 1947) is a retired Vietnam Air Force aviator and cosmonaut. He became the first Vietnamese citizen and the first person from an Asian country in space when he flew aboard the Soyuz 37 mission as an Interkosmos Research Cosmonaut. He was awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union.
He also downed the only B-52 the be downed in aerial combat. He was a really cool pilot.
If you ever want to make your own megathread, you can go here to reserve a spot! :xinternet:
Resources for Organizing your workplace/community :sabo:
Resources for Palestine :palestine-heart:
Buy coffee and learn more about the Zapatistas in Chiapas here :EZLN:
Here are some resources on Prison Abolition :brick-police:
Foundations of Leninism :USSR:
:lenin-shining: :unity: :kropotkin-shining:
Anarchism and Other Essays :ancom:
Remember, sort by new you :LIB:
Follow the Hexbear twitter account :comrade-birdie:
THEORY; it’s good for what ails you (all kinds of tendencies inside!) :RIchard-D-Wolff:
Come listen to music with your fellow Hexbears in Cy.tube :og-hex-bear:
Queer stuff? Come talk in the queer megathread!! :sicko-queer:
Monthly Neurodiverse Megathread and Monthly ND Venting Thread :Care-Comrade:

Julius Henry "Groucho" Marx (October 2, 1890 – August 19, 1977) was an American comedian, actor, writer, stage, film, radio, and television star. He is generally considered to have been a master of quick wit and one of America's greatest comedians.
He made 13 feature films as a team with his siblings the Marx Brothers, of whom he was the third-born. He also had a successful solo career, primarily on radio and television, most notably as the host of the game show You Bet Your Life.
His distinctive appearance, carried over from his days in vaudeville, included quirks such as an exaggerated stooped posture, spectacles, cigar, a thick greasepaint mustache, and eyebrows. These exaggerated features resulted in the creation of one of the most recognizable and ubiquitous novelty disguises, known as Groucho glasses: a one-piece mask consisting of horn-rimmed glasses, a large plastic nose, bushy eyebrows and mustache.
He was also secretly related to Karl Marx, the secret sixth Marx Brother.
Works of Theory by Groucho Marx
Beds
Beds: revised & updated edition
Many Happy Returns: An Unofficial Guide to Your Income-Tax Problems
Groucho and Me
Memoirs of a Mangy Lover
The Groucho Letters: Letters From and To Groucho Marx
The Marx Bros, Scrapbook
The Secret Word Is Groucho
The Groucho Phile: An Illustrated Life by Groucho Marx
Comprehensive list of resources for those in need of an abortion :feminism:
Resources for Palestine :palestine-heart:
Here are some resourses on Prison Abolition :brick-police:
Foundations of Leninism :USSR:
:lenin-shining: :unity: :kropotkin-shining:
Anarchism and Other Essays :ancom:
Remember, sort by new you :LIB:
Follow the Hexbear twitter account :comrade-birdie:
THEORY; it’s good for what ails you (all kinds of tendencies inside!) :RIchard-D-Wolff:
COMMUNITY CALENDAR - AN EXPERIMENT IN PROMOTING USER ORGANIZING EFFORTS :af:
Come listen to music with your fellow Hexbears in Cy.tube :og-hex-bear:
Queer stuff? Come talk in the Queer version of the megathread ! :sicko-queer:
Monthly Neurodiverse Megathread and Monthly ND Venting Thread :Care-Comrade:
Join the fresh and beautiful batch of new comms:
!labour@hexbear.net :iww:
!emoji@hexbear.net :meow-anarchist: :meow-tankie:
!libre@hexbear.net :libretion:
Now Introducing... The Six Marx Brothers!
:marx: :marx-goth: :marx-hi: :marx-joker: :marx-ok: :curious-marx:

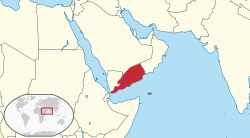
The People's Democratic Republic of Yemen was a socialist country that existed from 1967 to 1990 as a state in the Middle East in the southern and eastern provinces of the present-day Republic of Yemen, including the island of Socotra.
British rule
In 1838, Sultan Muhsin Bin Fadl of the state of Lahej ceded 194 km2 (75 sq. miles) including Aden to the British. On 19 January 1839, the British East India Company landed Royal Marines at Aden to occupy the territory and stop attacks by pirates against British shipping to India. It then became an important trading hub between British India and the Red Sea, and following the opening of the Suez canal in 1869, it became a coaling station for ships en route to India. Aden was ruled as part of British India until 1937, when the city of Aden became the Colony of Aden. The Aden hinterland and Hadhramaut to the east formed the remainder of what would become South Yemen and was not administered directly by Aden but were tied to Britain by treaties of protection with local rulers of traditional polities that, together, became known as the Aden Protectorate. Economic development was largely centered in Aden, and while the city flourished, the states of the Aden Protectorate stagnated.
Decolonization
In 1963, Aden and much of the Protectorate were joined to form the Federation of South Arabia with the remaining states that declined to join, mainly in Hadhramaut, forming the separate Protectorate of South Arabia. Both of these polities were still tied to Britain with promises of total independence in 1968. Two nationalist groups, the Front for the Liberation of Occupied South Yemen (FLOSY) and the National Liberation Front (NLF), began an armed struggle known as the Aden Emergency on 14 October 1963 against British control and, with the temporary closure of the Suez Canal in 1967, the British began to withdraw. One faction, NLF, was invited to the Geneva Talks to sign the independence agreement with the British. However, Britain - who during its occupation of Aden signed several treaties of protection with the local sheikhdoms and emirates of the Federation of South Arabia - excluded them in the talks and thus the agreement stated "...the handover of the territory of South Arabia to the (Yemeni) NLF...". Southern Yemen became independent as the People's Republic of Southern Yemen on 30 November 1967, and the National Liberation Front consolidated its control in the country.
In June 1969 a Marxist wing of the NLF gained power in an event known as the Corrective Move. This wing reorganized the country into the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (PDRY) on 30 November 1970. Subsequently, all political parties were amalgamated into the National Liberation Front, renamed the Yemeni Socialist Party. The People's Democratic Republic of Yemen established close ties with the Soviet Union, the People's Republic of China, Cuba, and the Palestinian Liberation Organization. East Germany's constitution of 1968 even served as a kind of blueprint for the PDRY's first constitution.
The new government embarked on a programme of nationalisation, introduced central planning, put limits on housing ownership and rent, and implemented land reforms. By 1973, the GDP of South Yemen increased by 25 percent. And despite the conservative environment and resistance, women became legally equal to men, polygamy, child marriage and arranged marriage were all banned by law. Equal rights in divorce were also sanctioned. The Republic also secularized education and sharia law was replaced by a state legal code.
The major communist powers assisted in the building of the PDRY's armed forces. Strong support from Moscow resulted in Soviet naval forces gaining access to naval facilities in South Yemen.
Daily Life in South Yemen
South Yemen's ethnic groups were ethnic Yemeni Arabs (92.8%), Somalis (3.7%), Afro-Arab 1.1%, Indians and Pakistanis (1%), and other (1.4%) (2000). The only recognised political party in South Yemen was the Yemeni Socialist Party, which ran the country and the economy along self-described Marxist lines, modeled on the Soviet Union.
Women's rights under the socialist government were considered the best in the region. Women became legally equal to men and were encouraged to work in public; polygamy, child marriage, and arranged marriage were all banned; and equal rights in divorce received legal sanction. The Supreme People's Council was appointed by the General Command of the National Liberation Front in 1971. In Aden, there was a structured judicial system with a Supreme Court. Education was paid for through general taxation. Income equality improved, corruption was reduced, and health and educational services expanded.
There was no housing crisis in South Yemen. Surplus housing meant that there were few homeless people in Aden, and people built their own houses out of adobe and mud in the rural areas. There was little industrial output, or mineral wealth exploitation, in South Yemen, until the mid-1980s, following the discovery of significant petroleum reserves in the central regions near Shibam and Mukalla. The main sources of income were agriculture, mostly fruit, cereal crops, cattle and sheep, fishing and later, oil exports.
South Yemen developed as a Marxist, mostly secular society ruled first by the National Liberation Front, which later morphed into the ruling Yemeni Socialist Party. The only avowedly Marxist nation in the Middle East, South Yemen received significant foreign aid and other assistance from the USSR and East Germany, which stationed several hundred officers of the Stasi in the country to train the nation's secret police and establish another arms trafficking route to Palestine. The East Germans did not leave until 1990, when the Yemeni government declined to pay their salaries which had been terminated with the dissolution of the Stasi during German reunification.
Disputes with North Yemen
Unlike the early decades of East Germany and West Germany, North Korea and South Korea, or North Vietnam and South Vietnam, the Yemen Arab Republic (North Yemen) and South Yemen (PDRY) remained relatively friendly, though relations were often strained. Fighting broke out in 1972, and a short-lived, small proxy border conflict was resolved with negotiations, where it was declared unification would eventually occur.
However, these plans were put on hold in 1979, as the PDRY funded Red rebels in the YAR, and war was only prevented by an Arab League intervention. The goal of unity was reaffirmed by the northern and southern heads of state during a summit meeting in Kuwait in March 1979.
In 1980, PDRY president Abdul Fattah Ismail resigned and went into exile in Moscow, having lost the confidence of his sponsors in the USSR. His successor, Ali Nasir Muhammad, took a less interventionist stance toward both North Yemen and neighbouring Oman.
Civil War
On January 13, 1986, a violent struggle began in Aden between Ali Nasir's supporters and supporters of the returned Ismail, who wanted power back. Fighting, known as the South Yemen Civil War, lasted for more than a month and resulted in thousands of casualties, Ali Nasir's ouster, and Ismail's death. Some 60,000 people, including the deposed Ali Nasir, fled to the YAR. Ali Salim al-Beidh, an ally of Ismail who had succeeded in escaping the attack on pro-Ismail members of the Politburo, then became General Secretary of the Yemeni Socialist Party.
Yemeni Unification
Against the background of the perestroika in the USSR, the main backer of the PDRY, political reforms were started in the late 1980s. Political prisoners were released, political parties were formed and the system of justice was reckoned to be more equitable than in the North. In May 1988, the YAR and PDRY governments came to an understanding that considerably reduced tensions including agreement to renew discussions concerning unification, to establish a joint oil exploration area along their undefined border, to demilitarize the border, and to allow Yemenis unrestricted border passage on the basis of only a national identification card. In 1990, the parties reached a full agreement on joint governing of Yemen, and the countries were effectively merged as Yemen.
After three years, however, a political crisis arose between the South's YSP and the North's GPC and Islah parties after the parliamentary elections in 1993. A year later, South Yemen declared its secession from the North Yemen in 1994 and a new, unrecognised secessionist state, the Democratic Republic of Yemen, which ended with its dissolution and the North Yemen occupying South Yemen after the 1994 civil war. 23 years later, another attempt to restore South Yemen (as only a country, not a socialist state) with the Southern Transitional Council as its new government began in 2017 and continues into the present day.
Roman Armenia refers to the rule of parts of Greater Armenia by the Roman Empire, from the 1st century AD to the end of Late Antiquity. In the late 4th century, Armenia was divided between Rome and the Sasanians, who took control of the larger part of the Armenian Kingdom and in the mid-5th century abolished the Armenian monarchy. In the 6th and 7th centuries, Armenia once again became a battleground between the East Romans (Byzantines) and the Sasanians, until both powers were defeated and replaced by the Muslim Caliphate in the mid-7th century.
In 363, a treaty was signed between the East Roman and Sassanid Persian empires, which divided Armenia between the two. The Persians retained the larger part of Armenia ("Persarmenia") while the Romans received a small part of Western Armenia.
Another treaty followed between 384 and 390, the Peace of Acilisene (usually dated c. 387), which established a definite line of division, running from a point just east of Karin (soon to be renamed Theodosiopolis) to another point southwest of Nisibis in Mesopotamia. The area under East Roman control thus increased, but still, about four fifths of the old Kingdom of Armenia remained under Persian rule.
Unlike Armenia Minor west of the Euphrates, which had been constituted into full provinces (Armenia I and Armenia II) under the Diocese of Pontus already in the time of Diocletian, the new territories retained a varying level of autonomy. Armenia Maior, the northern half, was constituted as a civitas stipendaria under a civil governor titled comes Armeniae, meaning that it retained internal autonomy, but was obliged to pay tribute and provide soldiers for the regular East Roman army.
Under Roman rule, Melitene was the base camp of Legio XII Fulminata. It was a major center in Armenia Minor (P'ok'r Hayk'), remaining so until the end of the 4th century. Emperor Theodosius I divided the region into two provinces: First Armenia (Hayk'), with its capital at Sebasteia (modern Sivas); and Second Armenia, with its capital at Melitene.
The Satrapies (Latin: Gentes) in the south on the other hand, which had been under Roman influence already since 298, were a group of six fully autonomous principalities allied to the Empire (civitates foederatae): Ingilene, Sophene, Antzitene, Asthianene, Sophanene and Balabitene. The local Armenian nakharar were fully sovereign in their territories, and were merely required to provide soldiers upon request and to dispatch a golden crown to the emperor, as a token of submission. In return, they received their royal insignia, including red shoes, from the emperor.
The situation remained unchanged for near a century, until a large-scale revolt by the satraps in 485 against Emperor Zeno (r. 474–491). In its aftermath, the satraps were stripped of their sovereignty and their rights of hereditary succession, being in effect reduced to the status of tax-paying and imperially-administered civitates stipendariae.
Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) carried out a series of comprehensive administrative reforms. Already soon after his accession in 527, the dux Armeniae (responsible for Armenia Minor) and the comes Armeniae were abolished, and the military forces of the Armenian territories were subordinated to a new magister militum per Armeniam at Theodosiopolis.
In 536, new reforms were enacted that abolished the autonomy of the trans-Euphrates territories and formed four new regular provinces. Armenia Interior was joined with parts of Pontus Polemoniacus and Armenia I to form a new province, Armenia I Magna, the old Armenia I and Armenia II were re-divided into Armenia II and Armenia III, and the old Satrapies formed the new Armenia IV province. In 538, the Armenian nobles rose up against heavy taxation, but were defeated and forced to find refuge in Persia.
In 591, the treaty between Khosrow II and Maurice ceded most of Persarmenia to the Eastern Roman Empire.
The region was the focus of prolonged warfare in the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. After the onset of the Muslim conquests and the Arab conquest of Armenia, only the western parts of Armenia remained in Byzantine hands, forming part of the theme of Armeniakon. Armenia remained dominated by the Arabs thereafter, and was ruled by a succession of Caliphate-appointed emirs as well as local princes.
With the ebbing of the Caliphate's power and the fracturing of its outlying territories into autonomous statelets, the Byzantines were able to re-assert their influence over the Armenian principalities during the campaigns of John Kourkouas in the early 10th century. In the first half of the 11th century, under Basil II and his successors, most of Armenia came under direct Byzantine control, which lasted until the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, when all Armenia fell to the Seljuks.
Roman Christianity
The influence of Christianity was felt in the 1st century after Christ: Christianity was first introduced by the apostles Bartholomew and Jude Thaddeus. Thus both Saints are considered the patron saints of the Armenian Apostolic Church.
Apostle Bartholomew is said to have been executed in Albanopolis in Armenia. According to popular hagiography, the apostle was flayed alive and beheaded. According to other accounts he was crucified upside down (head downward) like St. Peter. He is said to have been martyred for having converted Polymius, the king of Armenia, to Christianity. Enraged by the monarch's conversion, and fearing a Roman backlash, king Polymius's brother, prince Astyages, ordered Bartholomew's torture and execution, which Bartholomew courageously endured. However, there are no records of any Armenian King of the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia with the name Polymius. Current scholarship indicates that Bartholomew more likely died in Kalyan in India, where there was an official named Polymius.
Armenia became the first country to establish Christianity as its state religion when, in an event traditionally dated to 301, Gregory the Illuminator convinced Tiridates III, the king of Armenia, to convert to Christianity.
As a consequence of Diocletian's victory over the Sassanids, all of Armenia was once again a vassal state of Rome by 299: Rome secured in this way a wide zone of cultural influence east of Anatolia, which led to a wide diffusion of Syriac Christianity from a center at Nisibis in the first decades of the 4th century, and to the eventual full Christianization of Armenia.
Before this, the dominant religion in Armenia was Zoroastrianism (promoted by the Parthian/Sassanid Empire) and to a smaller degree local Paganism. St Gregory and his son Aristaces were successful in the full Christianization of all Armenians in the first half of the 4th century, mainly after Roman emperor Constantine legalised Christianity in the Roman Empire in 313.
It is a well recognized historical fact that the Armenians were the first nation in the world to formally adhere to Christianity. This conversion was followed in the 4th and 5th centuries by a process of institutionalization and Armenization of Christianity in Armenia. Indeed, Gregory the Illuminator became the organizer of the Armenian Church hierarchy. From that time, the heads of the Armenian Church have been called Catholicos and still hold the same title.
St. Gregory chose as the site of the "Catholicosate" the capital city of Vagharshapat (actual Ejmiatsinin) in Armenia and built there the Etchmiadzin Cathedral as a vaulted basilica in 301-303 (Vahan Mamikonian, Roman governor of Armenia, in 480 ordered the dilapidated basilica to be replaced with a new cruciform church, still standing in the modern Armenia).
The continuous upheavals, which characterized the political scenes of Armenia in the next centuries, made the political power move to safer places often related to the Eastern Roman Empire. The Church center moved as well to different locations together with the political authority, ending in Byzantine Cilicia in the 13th century.







P good, got a decent job, moved in with my gf almost a year ago now. Haven't been posting as much, but is what it is I suppose lol